After months of living under the looming threat of “Day Zero”, Cape Town has tentatively pushed back the deadline of extreme water crisis for the remainder of the year. Day Zero, which had originally been scheduled for April 22, reflects the date when water levels in the city's major dams reaches 13.5% of their capacity. If this day arrived, taps would be shut off and Cape Town residents would need to stand in line to pick up their 25-liter daily ration of water.1 For perspective, this equivalent to the amount of water consumed in a four-minute shower.2
Drought-driven water shortages are a worldwide crisis. The cities at highest risk to run out of water include Jakarta (where the city is sinking from illegal groundwater extraction as sea levels around it rise), Mexico City (where taps are already turned off for many city citizens for parts of the day), Tokyo, London, and Miami.3 In California, almost 50% of the state is currently experiencing
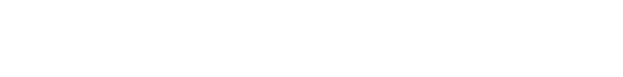








![Join Sterlitech at BIO 2024 [Booth #5558]: Exploring the Future of Biotechnology](https://www.sterlitech.com/media/magefan_blog/b4.jpeg)

