What is membrane “wet-ability”? Hydrophilic PCTE membranes explained
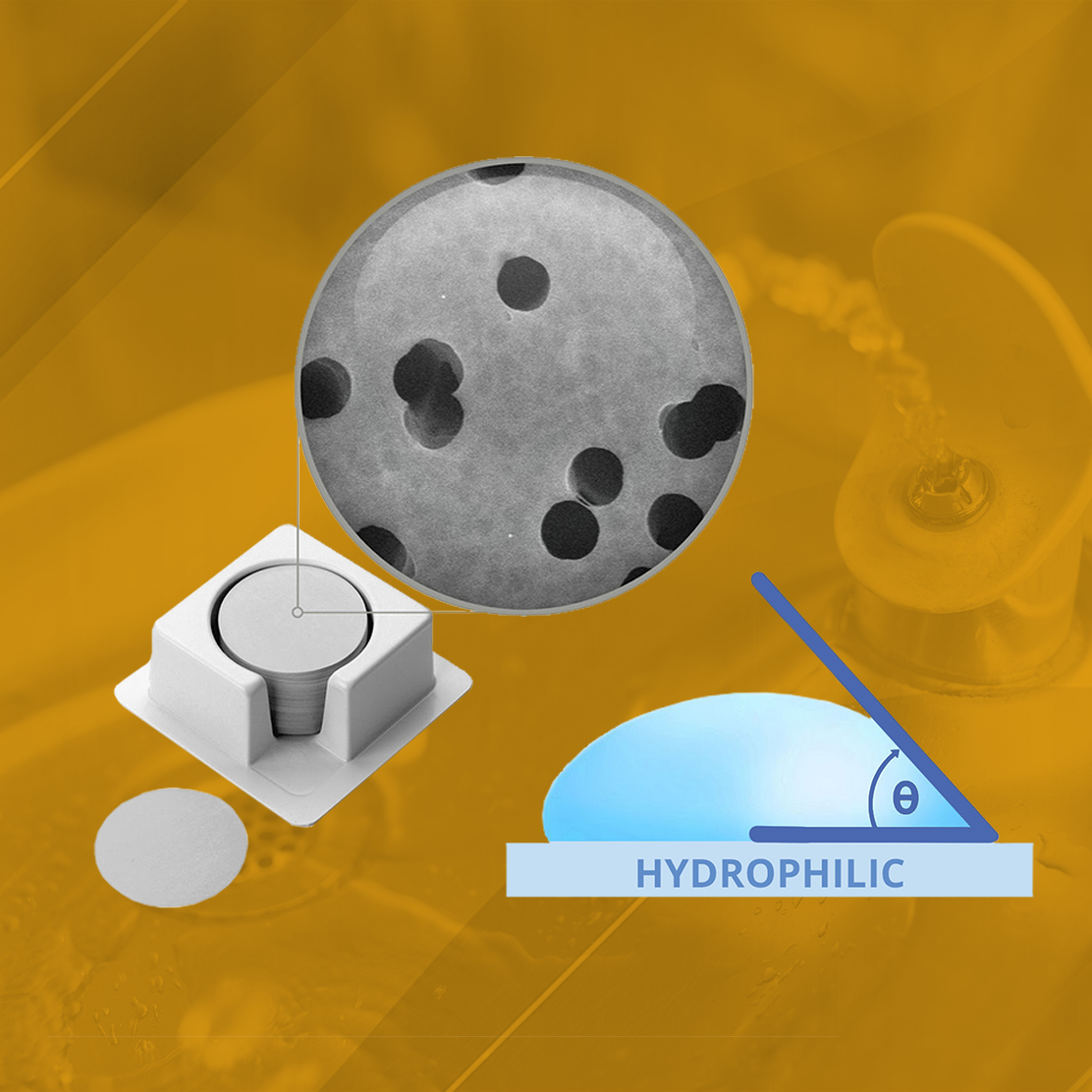
What is a hydrophilic PCTE membrane?
Polycarbonate track-etched (PCTE) membranes are characterized by durability, low protein binding, controlled porosity, and surface smoothness. PCTE membranes come in hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials, which affects the membrane “wet-ability”. Wet-ability refers to the ability of a membrane to draw water into the pore structure. Hydrophilic PCTE membranes have a high “wet-ability”, which means that the water contact angle is less than 90 degrees. As a water droplet is drawn through the membrane by capillary action, the water contact angle decreases. Hydrophilic membranes are best used for applications with aqueous solutions such as cell culturing, biological assays, and sterilization.
How to improve wet-ability?
For membrane filter applications that require high “wet-ability”, the hydrophilic nature of a membrane can be improved with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) coating. PVP coated PCTE membranes have extractable-minimizing properties and are ideal for biological assays and high-purity general filtration. However, PVP coatings may interfere with some applications, such as cell attachment.
- Most Viewed Blog Articles (5)
- Company News (284)
- Emerging Technologies (64)
- Microbiology and Life Science News (93)
- Water and Fluid Separation News (97)
- Filtration Resources (93)
- Product News (19)

![Join Sterlitech at BIO 2024 [Booth #5558]: Exploring the Future of Biotechnology](https://www.sterlitech.com/media/blog/cache/300x200/magefan_blog/b4.jpeg)