SterliTECH Tip: Why is Cross-Flow Velocity (CFV) a Key Test Parameter to Investigate?
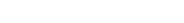
Cross-Flow Velocity (CFV) is the linear velocity of the flow tangential to the membrane surface and is reported in [m/sec] or [ft/sec]. It refers to the velocity at which a fluid or gas flows across a solid surface or through a porous medium. It is a key test parameter to investigate in various fields and applications due to its significant impact on fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and mass transfer processes. Cross-Flow Velocity (CFV) is calculated by dividing the volumetric flow rate [lpm or gpm] in the flow channel by the cross sectional area [m² or ft²] of the flow channel.
Here are a few reasons why CFV is an important parameter to consider:
- CFV impacts solute percent rejection by increasing or decreasing gel-layer formation.
- CFV impacts the permeation flow rate.
- CFV provides pressure drop data for determining the maximum number of membrane elements in series for process scale up design.
- CFV data will help in determining pump design and energy consumption for scale-up design.
For homogeneous aqueous solutions, investigate velocities: 0.1-0.5 m/sec
For slurry type solutions, and solutions having greater than 1000 mg/L of Total Suspended Solids (TSS) investigate velocities 0.5- 2 m/sec.
Note: Always review the maximum differential pressure for the membrane configuration being tested.
Overall, CFV is a key test parameter because it directly influences the performance, efficiency, and integrity of systems involving fluid flow. By investigating CFV, engineers and researchers can optimize designs, improve process understanding, and develop innovative solutions for a wide range of applications.
- Most Viewed Blog Articles (5)
- Company News (285)
- Emerging Technologies (64)
- Microbiology and Life Science News (93)
- Water and Fluid Separation News (97)
- Filtration Resources (93)
- Product News (19)

![Join Sterlitech at BIO 2024 [Booth #5558]: Exploring the Future of Biotechnology](https://www.sterlitech.com/media/blog/cache/300x200/magefan_blog/b4.jpeg)